Therapeutic Focus

Types of hair loss
There are different types of hair loss, including male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia), female pattern baldness, alopecia areata (patchy hair loss), telogen effluvium (temporary hair shedding), and traction alopecia (caused by excessive pulling or tension on the hair).
Causes of hair loss
Hair loss can have various causes, including genetics, hormonal changes (such as dihydrotestosterone in male pattern baldness), autoimmune conditions (as in alopecia areata), certain medications, nutritional deficiencies, stress, and certain hairstyles or hair treatments that cause damage or traction.

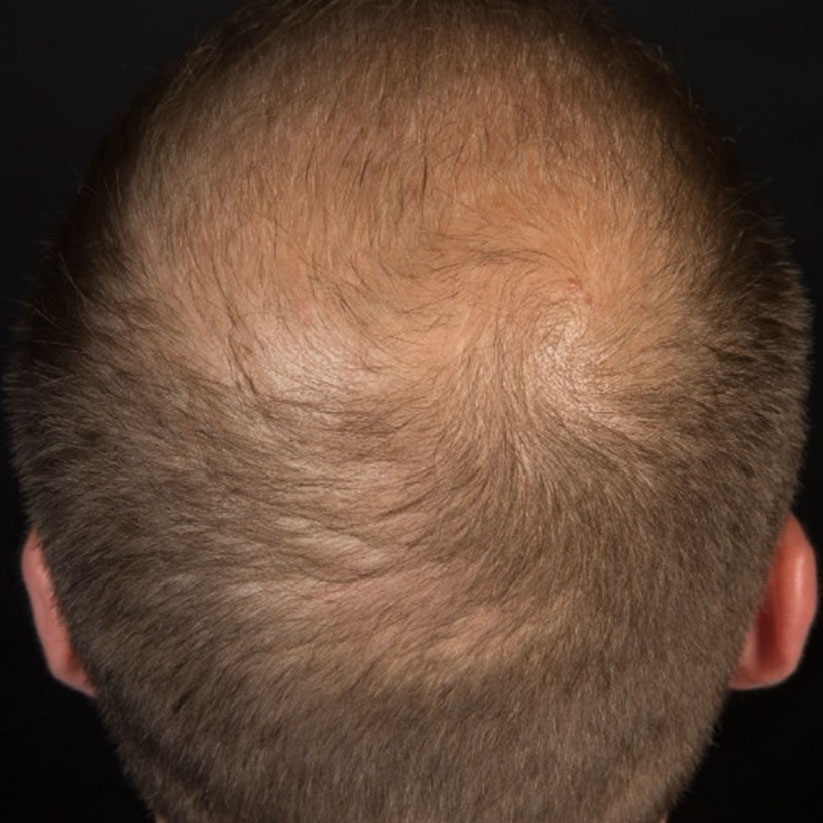
Pattern and progression
Male pattern baldness typically follows a specific pattern, starting with hair thinning at the temples and crown and gradually progressing to partial or complete baldness. Female pattern baldness often results in overall hair thinning. Other types of hair loss may appear as patchy or diffuse hair loss.
Psychological impact
Hair loss can have significant psychological and emotional effects on individuals, impacting self-esteem, body image, and overall well-being. Support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or counseling may be beneficial for individuals experiencing distress related to hair loss.

Indication
1. Androgenetic Alopecia
Also known as male or female pattern baldness, this is the most common type of alopecia. It typically occurs gradually and is related to genetic and hormonal factors. In men, it often results in a receding hairline and baldness on the top of the head. In women, it leads to thinning hair on the crown of the head.
2. Alopecia Areata
This type of alopecia causes patchy hair loss on the scalp, face, or other parts of the body. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, resulting in an autoimmune mediated hair loss. The hair can grow back spontaneously, but it may also fall out again.
3. Alopecia Totalis and Alopecia Universalis
These are more extensive forms of alopecia areata. Alopecia totalis causes the complete loss of hair on the scalp, while alopecia universalis leads to hair loss on the entire body, including the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair.
4. Telogen Effluvium
This type of alopecia occurs when a significant number of hair follicles enter the resting phase (telogen) prematurely, resulting in increased hair shedding. It can be triggered by various factors such as stress, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions.
5. Traction Alopecia
This form of alopecia is caused by repetitive pulling or tension on the hair, often due to hairstyles like tight braids, ponytails, or hair extensions. The constant pulling damages the hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
6. Scarring Alopecia
Also known as cicatricial alopecia, this type involves the destruction of hair follicles and subsequent scarring. It can be caused by various conditions like autoimmune disorders, infections, or inflammatory skin conditions.